
 Mondrian – abstracting out of nature.
Mondrian – abstracting out of nature.
Perhaps there is something of the universe in all of these above.
Abstraction Rules OK.
Shut the F up!
Just buy the book!
https://www.smashwords.com/books/search?query=siri+perera
Society is an evolutionary tool created by the mind to see itself.
http://www.lulu.com/shop/search.ep?type=&keyWords=siri+perera&x=-1&y=9&sitesearch=lulu.com&q=
steal millions from bank – Santander
1 computer with 1 IP address – where is the problem with that when a whole network in a bank is vulnerable and your mind that is even easier. You silently talk when you think – “Speak Thinking” listening in to your thinking – is it possible?
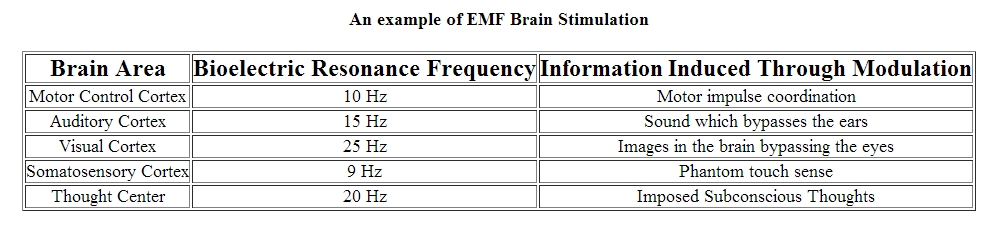
Hacking into the mind might today be a real possibility after about 50 years of trying to make it work. Bypassing the 5 external sensors of the body that monitors your reality and going straight for the parts in the brain that processes the various sensory information. Penetrative short wave EMF waves could be used to access the brain but remotely.
Types of Brain Imaging Techniques
By MICHAEL DEMITRI, M.D.
Brain imaging techniques allow doctors and researchers to view activity or problems within the human brain, without invasive neurosurgery. There are a number of accepted, safe imaging techniques in use today in research facilities and hospitals throughout the world.
fMRI
Functional magnetic resonance imaging, or fMRI, is a technique for measuring brain activity. It works by detecting the changes in blood oxygenation and flow that occur in response to neural activity – when a brain area is more active it consumes more oxygen and to meet this increased demand blood flow increases to the active area. fMRI can be used to produce activation maps showing which parts of the brain are involved in a particular mental process.
CT
Computed tomography (CT) scanning builds up a picture of the brain based on the differential absorption of X-rays. During a CT scan the subject lies on a table that slides in and out of a hollow, cylindrical apparatus. An x-ray source rides on a ring around the inside of the tube, with its beam aimed at the subjects head. After passing through the head, the beam is sampled by one of the many detectors that line the machine’s circumference. Images made using x-rays depend on the absorption of the beam by the tissue it passes through. Bone and hard tissue absorb x-rays well, air and water absorb very little and soft tissue is somewhere in between. Thus, CT scans reveal the gross features of the brain but do not resolve its structure well.
PET
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) uses trace amounts of short-lived radioactive material to map functional processes in the brain. When the material undergoes radioactive decay a positron is emitted, which can be picked up be the detector. Areas of high radioactivity are associated with brain activity.
EEG
Electroencephalography (EEG) is the measurement of the electrical activity of the brain by recording from electrodes placed on the scalp. The resulting traces are known as an electroencephalogram (EEG) and represent an electrical signal from a large number of neurons.
EEGs are frequently used in experimentation because the process is non-invasive to the research subject. The EEG is capable of detecting changes in electrical activity in the brain on a millisecond-level. It is one of the few techniques available that has such high temporal resolution.
MEG
Magnetoencephalography (MEG) is an imaging technique used to measure the magnetic fields produced by electrical activity in the brain via extremely sensitive devices known as SQUIDs. These measurements are commonly used in both research and clinical settings. There are many uses for the MEG, including assisting surgeons in localizing a pathology, assisting researchers in determining the function of various parts of the brain, neurofeedback, and others.
NIRS
Near infrared spectroscopy is an optical technique for measuring blood oxygenation in the brain. It works by shining light in the near infrared part of the spectrum (700-900nm) through the skull and detecting how much the remerging light is attenuated. How much the light is attenuated depends on blood oxygenation and thus NIRS can provide an indirect measure of brain activity.






Aw, this was an exceptionally good post. Taking the time and actual effort
to produce a great article… but what can I say… I put things off
a lot and never seem to get anything done.